Can Apps and Wearables Replace Doctors? The Promise and Limitations
“From pocket physicians to wearable health guardians, the rise of health apps and wearables promises to revolutionize healthcare.”
Key Takeaways:
- Health apps and wearables offer remote monitoring and real-time data collection.
- They empower patients for self-care and early detection of health issues.
- These technologies improve healthcare access and affordability.
- Data accuracy and privacy are vital for user trust.
- They complement, not replace, doctors’ expertise and personalized care.
- Ethical considerations are essential in handling sensitive health data.
- Advancements in AI enhance personalized insights and predictions.
- Integrating into healthcare systems enhances patient-centric care.
- Collaboration and responsible use maximize their potential for better health.
In today’s fast-paced world, where technology is seamlessly integrated into every aspect of our lives, it is no surprise that our health is tapping into the digital age. Health apps and wearables, those nifty little companions residing in our smartphones and adorning our wrists, have emerged as game-changers in healthcare. They promise to empower us, enabling a more proactive approach to well-being, and some even dare to pose the question: Can they replace doctors?
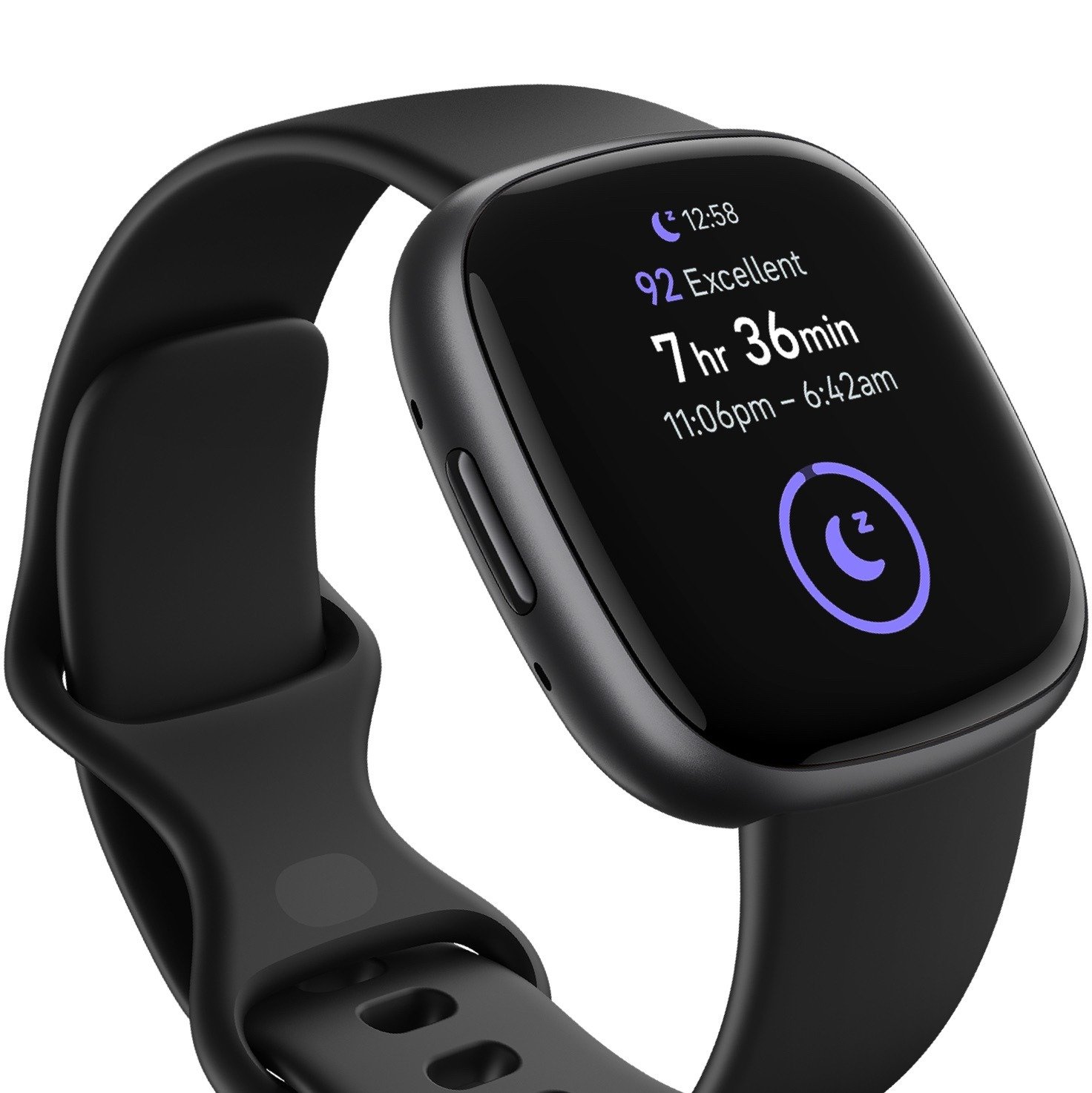
Health apps and wearables are the digital emissaries of self-care, offering a treasure trove of data and insights about our bodies and minds. The former are software applications downloaded onto smartphones, while the latter are smart devices equipped with sensors, tracking everything from heartbeats to sleep patterns. Together, they form a dynamic duo, equipping us with the tools to monitor and manage our health with newfound precision and personalization.
Their allure has not gone unnoticed, and they have witnessed an unprecedented surge in popularity and adoption within the healthcare landscape. From fitness enthusiasts to individuals grappling with chronic health conditions, millions now wield these digital companions as trusty sidekicks in pursuing healthier lives.
As we peer deeper into health apps and wearables, it becomes evident that these digital marvels offer compelling promises, redefining how we interact with our health. The convenience they bring is undeniable, granting us the power to track vital health metrics in real-time, right at our fingertips. From monitoring heart rates during workouts to assessing sleep patterns, these intuitive applications serve as vigilant guardians of our well-being.
Moreover, empowerment takes center stage in this digital health revolution. Health apps and wearables firmly put the steering wheel of health in our grasp, empowering us to become proactive participants in our care. Through personalized insights and data-driven feedback, we are better equipped to make informed decisions, adopt healthier habits, and even detect potential health issues in their infancy. Early detection could be a life-saving advantage, prompting timely interventions that might have slipped under the radar.
Furthermore, these digital companions’ growing popularity and widespread adoption have significantly expanded their horizons. Beyond fitness enthusiasts and wellness warriors, health apps and wearables have found their place in the management of chronic diseases. Patients grappling with conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma now have access to tailored solutions for monitoring their health parameters, arming them with essential information to collaborate with their healthcare providers in fine-tuning treatment plans.
Yet, as we laud the promises offered by health apps and wearables, we must tread cautiously and acknowledge their inherent limitations. While these digital tools excel at data collection and analysis, they may need to improve at providing the human touch so vital in medicine. The compassionate bedside manner, the reassuring presence during difficult times, and the ability to read subtle nuances in a patient’s demeanor remain uniquely human attributes that technology cannot replicate.
Moreover, questions surrounding the accuracy and reliability of the data generated by these digital allies loom large. Variances in sensor precision or user error could lead to misinterpretations or false alarms, possibly causing unnecessary anxiety or delayed medical attention. Hence, distinguishing between trusting these technologies and seeking expert medical advice becomes essential in navigating our health journey.
Ethical considerations must also find their place in the discourse. As health apps and wearables gather vast amounts of sensitive health data, questions arise concerning data privacy, security, and consent. Striking the right balance between data sharing for medical research and safeguarding individual privacy remains an ongoing challenge for the healthcare community and policymakers.
The Promise of Apps and Wearables in Healthcare
Remote Monitoring and Real-time Data Collection
The promise of health apps and wearables in healthcare lies in their ability to enable remote monitoring and real-time data collection. These digital companions serve as vigilant health guardians, continuously tracking vital health metrics and providing immediate feedback. Remote monitoring becomes a game-changer for patients with chronic conditions or those in post-operative recovery. Healthcare providers can receive real-time updates on their patient’s health status, allowing for timely interventions and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits. This real-time data empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and gives patients greater peace of mind, knowing that their health is being closely monitored.
Empowering Patients for Self-Care
One of the most transformative promises of health apps and wearables is their ability to empower patients with self-care. These technologies put the reins of health management firmly in the hands of individuals, promoting a proactive approach to well-being. With personalized insights and data-driven feedback, users can better understand their health trends and lifestyle habits. Armed with this knowledge, they can adopt healthier behaviors, set achievable goals, and make informed decisions about their health. Empowered patients become active partners in their healthcare journey, working collaboratively with healthcare providers to achieve better outcomes.
Early Detection and Prevention of Health Issues
Health apps and wearables offer the potential for early detection and prevention of health issues, revolutionizing the healthcare landscape. By continuously monitoring health metrics and identifying deviations from normal patterns, these technologies can alert users and healthcare professionals to potential health risks before symptoms manifest. This early warning system could be especially impactful in managing chronic diseases and preventing complications. Moreover, health apps and wearables can nudge users towards healthy choices by encouraging physical activity, promoting better sleep, or suggesting stress reduction techniques.
Improving Healthcare Access and Affordability
Another promise of health apps and wearables is improving healthcare access and affordability. These technologies break down geographical barriers, providing healthcare services and information to individuals regardless of location. Telehealth services, enabled by remote monitoring through apps and wearables, offer greater access to medical expertise and consultations. This improved accessibility can be a boon for individuals in remote or underserved areas. Additionally, health apps and wearables have the potential to reduce healthcare costs by facilitating preventive care and early interventions, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and lower medical expenses.
Limitations and Challenges
Accuracy and Reliability of Data
While health apps and wearables offer great promise, their accuracy and reliability of data remain critical challenges. Precisely calibrating sensors and algorithms is essential for generating trustworthy health insights. Variances in sensor accuracy or user error can lead to misinterpretations or false alarms, potentially causing unnecessary anxiety or delayed medical attention. Striking a balance between technological advancement and ensuring accurate data representation is crucial in gaining user trust and confidence in these digital health tools.
Lack of Personalized Care
One of the limitations of health apps and wearables is their potential to fall short in providing the human touch and personalized care that doctors offer. While these technologies can offer valuable data-driven insights, they cannot fully replace the empathetic and individualized approach that healthcare professionals bring to patient care. The human element of medicine, such as understanding the patient’s emotional state, cultural background, and unique health needs, remains indispensable and must complement the role of digital health technologies.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
As health apps and wearables gather vast amounts of sensitive health data, ethical and privacy concerns emerge. Users must trust that their data is being handled securely and used responsibly. Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and implementing robust security measures is essential to safeguarding user privacy. Healthcare providers and app developers must be transparent about data usage and seek explicit user consent to build and maintain trust between users and the digital health ecosystem.
Over-reliance and Misinterpretation of Results
A potential limitation of health apps and wearables is the risk of over-reliance and misinterpretation of results. Users may become overly dependent on these technologies, leading to a detachment from professional medical advice. It is crucial to strike a balance between using these tools for proactive self-care and seeking expert medical guidance when necessary. Furthermore, users must be educated about the limitations of health apps and wearables to prevent misinterpretation of data and self-diagnosis, which could have adverse health consequences.
Current Use Cases and Success Stories
Chronic Disease Management
In chronic disease management, health apps and wearables have shown promising results. Patients with diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease can use these technologies to monitor their health parameters regularly. By doing so, they can detect deviations from their baseline, enabling timely intervention and better disease management. These digital companions also offer educational resources and medication reminders, empowering patients to manage their conditions actively.
Fitness and Wellness Tracking
Health apps and wearables have become indispensable companions for fitness enthusiasts and individuals striving for overall wellness. These technologies can track physical activities, calories burned, and sleep patterns, giving users insights into their fitness levels and sleep quality. By setting personalized goals and receiving real-time feedback, individuals can stay motivated and make informed choices to improve their well-being.
Mental Health Support
Health apps and wearables are also making headway in supporting mental health. From meditation and mindfulness apps to sleep trackers that assess sleep quality, these tools offer valuable resources to help individuals manage stress, anxiety, and other mental health concerns. The availability of such resources at users’ fingertips fosters greater self-awareness and helps break down mental health stigma.
The Role of Apps and Wearables in Healthcare Ecosystem
Complementary Tool for Doctors and Healthcare Professionals
Rather than aiming to replace doctors, health apps and wearables should be embraced as complementary tools within the healthcare ecosystem. Healthcare professionals can leverage the wealth of data these technologies collect to gain deeper insights into patients’ health trends, enabling more personalized treatment plans. Combining medical expertise and data-driven insights can lead to better health outcomes and a more holistic approach to patient care.
Enhancing Patient-Doctor Communication
Health apps and wearables have the potential to enhance patient-doctor communication significantly. Patients can share real-time health data with their healthcare providers, allowing for more informed discussions during consultations. This data-driven approach enables a deeper understanding of the patient’s health status, treatment progress, and potential areas of concern. Improved communication fosters a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare professionals, empowering patients to participate in their care decisions actively.
Supporting Healthcare Research and Population Health
The data collected through health apps and wearables can also be vital in healthcare research and population health studies. Aggregated and anonymized data can offer valuable insights into health trends, disease prevalence, and risk factors on a large scale. By contributing to population health initiatives, these digital tools can support the development of targeted public health interventions and policies.
Regulatory Landscape and Quality Standards
FDA and Medical Device Regulations
As health apps and wearables become increasingly prevalent in healthcare, regulatory oversight is critical to ensuring their safety and efficacy. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory authority overseeing medical devices, including certain health apps and wearable devices. Depending on their intended use and functionality, some health apps and wearables may be classified as medical devices and require FDA clearance or approval.
The FDA’s regulatory process assesses the device’s intended use, risk classification, and performance data. For instance, health apps and wearables used for diagnostic purposes, treatment decisions, or monitoring of critical health conditions may be subject to a more rigorous regulatory pathway. On the other hand, those aimed at general health and wellness tracking may fall under less stringent regulations.
Navigating the FDA’s regulatory process can be complex for app developers and manufacturers. It requires a thorough understanding of the FDA’s guidelines and standards and extensive clinical data to support the device’s safety and effectiveness. Compliance with these regulations ensures that health apps and wearables meet the necessary quality standards and instill confidence in healthcare professionals and users regarding their reliability and accuracy.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy Compliance
The widespread adoption of health apps and wearables has led to an unprecedented influx of personal health data. As these technologies continuously collect and transmit sensitive information, ensuring data security and privacy compliance is paramount. The potential for data breaches or unauthorized access to health information raises significant ethical and legal concerns.
Healthcare providers, app developers, and device manufacturers must implement robust data security measures to protect users’ privacy. Encryption, secure data storage, and stringent access controls are vital components of a comprehensive data security strategy. Additionally, compliance with relevant data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, is essential to safeguarding users’ health information.
Transparency in data collection and use is equally critical. Users must be fully informed about the collected data, how it will be used, and their options for opting in or out of data sharing. Transparent privacy policies and consent mechanisms help build trust between users and the digital health ecosystem.
The Future Outlook
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The future of health apps and wearables holds tremendous potential with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies can significantly enhance the capabilities of these digital companions, enabling more sophisticated data analysis and predictive modeling. AI-powered algorithms can detect subtle health patterns and trends that might go unnoticed by traditional methods, leading to earlier detection of health issues and more targeted interventions.
Machine learning algorithms can also customize recommendations and insights based on individual health data, tailoring health advice to specific user needs. ML algorithms’ continuous learning and adaptability enable health apps and wearables to evolve with users’ changing health circumstances, further optimizing their potential for personalized healthcare.
Integration into Healthcare Systems
Health apps and wearables demonstrate their value in promoting proactive health management, so healthcare systems are increasingly embracing their integration. Electronic health record (EHR) systems incorporate data from these digital tools, providing a comprehensive view of patients’ health status to healthcare providers. This integration streamlines care coordination and facilitates data-driven decision-making in clinical settings.
Moreover, health apps and wearables are also pivotal in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. As telehealth services expand, health apps and wearables offer a bridge between patients and healthcare providers, enabling real-time monitoring and virtual consultations. This integration ensures that healthcare is not confined to the confines of a hospital or clinic but extends into patients’ daily lives.
Potential Impact on Healthcare Delivery
The integration of health apps and wearables into healthcare delivery has the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered. These technologies can facilitate a shift from reactive, episodic care to proactive, continuous care. Empowering patients to take charge of their health and providing healthcare professionals with valuable data, health apps, and wearables foster a more collaborative and patient-centric approach to healthcare.
The potential impact extends beyond individual patient care. Aggregated and anonymized data from health apps and wearables can contribute to population health studies and healthcare research. Analyzing vast datasets can reveal health trends and disease patterns, informing public health strategies and interventions.
However, as health apps and wearables become more deeply integrated into healthcare systems, addressing any existing disparities in access and adoption is crucial. Ensuring these technologies reach underserved populations and vulnerable communities is essential to achieving equitable and inclusive healthcare outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, health apps and wearables hold immense promise in transforming the healthcare landscape. These digital companions offer myriad benefits, ranging from remote monitoring and real-time data collection to empowering patients for self-care and enabling early detection and prevention of health issues. Moreover, they can potentially improve healthcare access and affordability, breaking down barriers and reaching individuals in remote or underserved areas.
The empowerment that health apps and wearables offer cannot be overstated. Providing users with personalized insights and data-driven feedback inspires individuals to become proactive partners in their health journey. These technologies allow individuals to take charge of their well-being, make informed decisions, and actively engage in preventive measures. The potential to detect health issues at their nascent stages can be life-saving, reducing the burden of chronic diseases and minimizing healthcare costs.
However, it is crucial to recognize and address the limitations and challenges that accompany these digital allies. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data generated by health apps and wearables is vital to preventing misinterpretation and false alarms. The human element of medicine, characterized by personalized care and empathy, remains irreplaceable, and striking the right balance between technology and human expertise is essential.
Ethical considerations and data privacy concerns must be at the forefront of the digital health revolution. Building trust in these technologies is critical to safeguarding users’ sensitive health information and communicating openly about data usage. Compliance with regulatory standards, such as those set by the FDA, ensures that health apps and wearables meet necessary quality requirements and inspire confidence in users and healthcare professionals.
The future outlook of health apps and wearables is filled with exciting possibilities. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning will further enhance the capabilities of these technologies, enabling more sophisticated data analysis and personalized insights. Integration into healthcare systems will continue to break down the barriers between patients and healthcare providers, fostering a seamless, continuous approach to care.
While health apps and wearables can never replace the expertise and compassion of doctors, they have the potential to be valuable complementary tools in the healthcare ecosystem. By combining the strengths of technology with the human touch of medicine, we can create a future where individuals are empowered, proactive, and engaged in their health and well-being.
In the journey towards a more patient-centric and data-driven healthcare system, collaboration and responsible implementation of health apps and wearables are essential. Embracing these digital companions while remaining mindful of their limitations will unlock technology’s true potential in transforming healthcare, shaping a future where health and well-being are within everyone’s grasp. As we navigate the digital frontier in medicine, the harmonious synergy between technology and humanity will pave the way for a healthier and more equitable world.