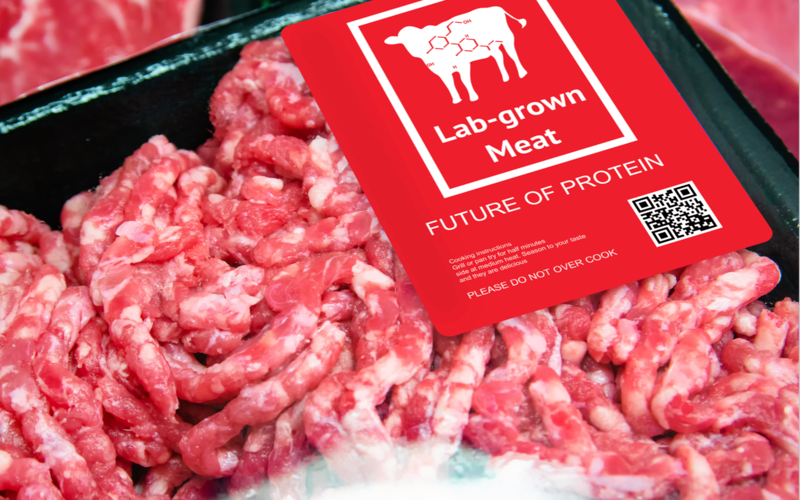
Lab-grown meat, a groundbreaking innovation in the food industry, has emerged as a promising solution to mitigate the environmental impact of conventional meat production. As an authoritative source, we aim to provide comprehensive insights into the intersection of lab-grown meat and climate change. This article explores the potential of lab-grown meat to revolutionize food production, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and address the challenges associated with climate change.
Understanding Lab-Grown Meat
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cultivated meat, is produced through a process involving growing animal cells in a controlled laboratory environment. This innovative approach offers a sustainable alternative to traditional livestock farming, significantly contributing to global greenhouse gas emissions.
The Environmental Benefits of Lab-Grown Meat
Lab-grown meat has the potential to reduce the environmental impact of meat production significantly. Cultivating meat in controlled environments can minimize the need for vast amounts of land, water, and resources associated with traditional livestock farming. This reduction in resource consumption positively affects deforestation, water scarcity, and biodiversity loss.
Moreover, lab-grown meat production emits fewer greenhouse gases than conventional meat production. The process eliminates the methane emissions associated with livestock farming, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to global warming. By reducing these emissions, lab-grown meat offers a more sustainable and climate-friendly approach to meat production.
Addressing Challenges and Improving Sustainability
While lab-grown meat holds great promise, some challenges must be addressed to ensure its long-term sustainability and effectiveness in combating climate change.
- Scaling Up Production
One of the key challenges is scaling up lab-grown meat production to meet the demands of a growing population. Currently, production capacities are limited compared to traditional meat facilities. However, companies like Eat Just and Upside Foods are making significant progress in developing larger-scale facilities to bring lab-grown meat to the market.
- Emissions and Energy Use
To maximize the environmental benefits of lab-grown meat, addressing emissions and energy use throughout the production process is crucial. Different production methods and technologies can yield varying emission levels. It is important to optimize processes to minimize energy consumption and emissions, such as exploring renewable energy sources and improving production efficiencies.
- Supply Chain and Ingredients
The lab-grown meat industry must also consider the sustainability of its supply chain and ingredients. It is essential to source ingredients responsibly, ensuring they are obtained from sustainable and environmentally friendly sources. Additionally, efforts should be made to reduce the environmental impact of packaging and transportation associated with lab-grown meat.
Future Prospects and Implications
As the lab-grown meat industry evolves, the future looks promising for sustainable food production and combating climate change. Advances in technology, research, and investment are driving the industry forward, with the potential for lab-grown meat to become a mainstream food choice.
Regulatory bodies, policymakers, and industry stakeholders play a critical role in shaping the future of lab-grown meat. Collaboration and dialogue are necessary to establish standards, ensure safety, and promote the adoption of lab-grown meat as a viable solution to address climate change and global food security.
Conclusion
Lab-grown meat represents a revolutionary approach to sustainable food production that has the potential to mitigate the environmental impact of traditional meat production. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, minimizing resource consumption, and improving the efficiency of food production, lab-grown meat offers a promising solution to combat climate change. While challenges remain, ongoing research, technological advancements, and industry initiatives pave the way for a future where lab-grown meat is vital in creating a sustainable and resilient food system.