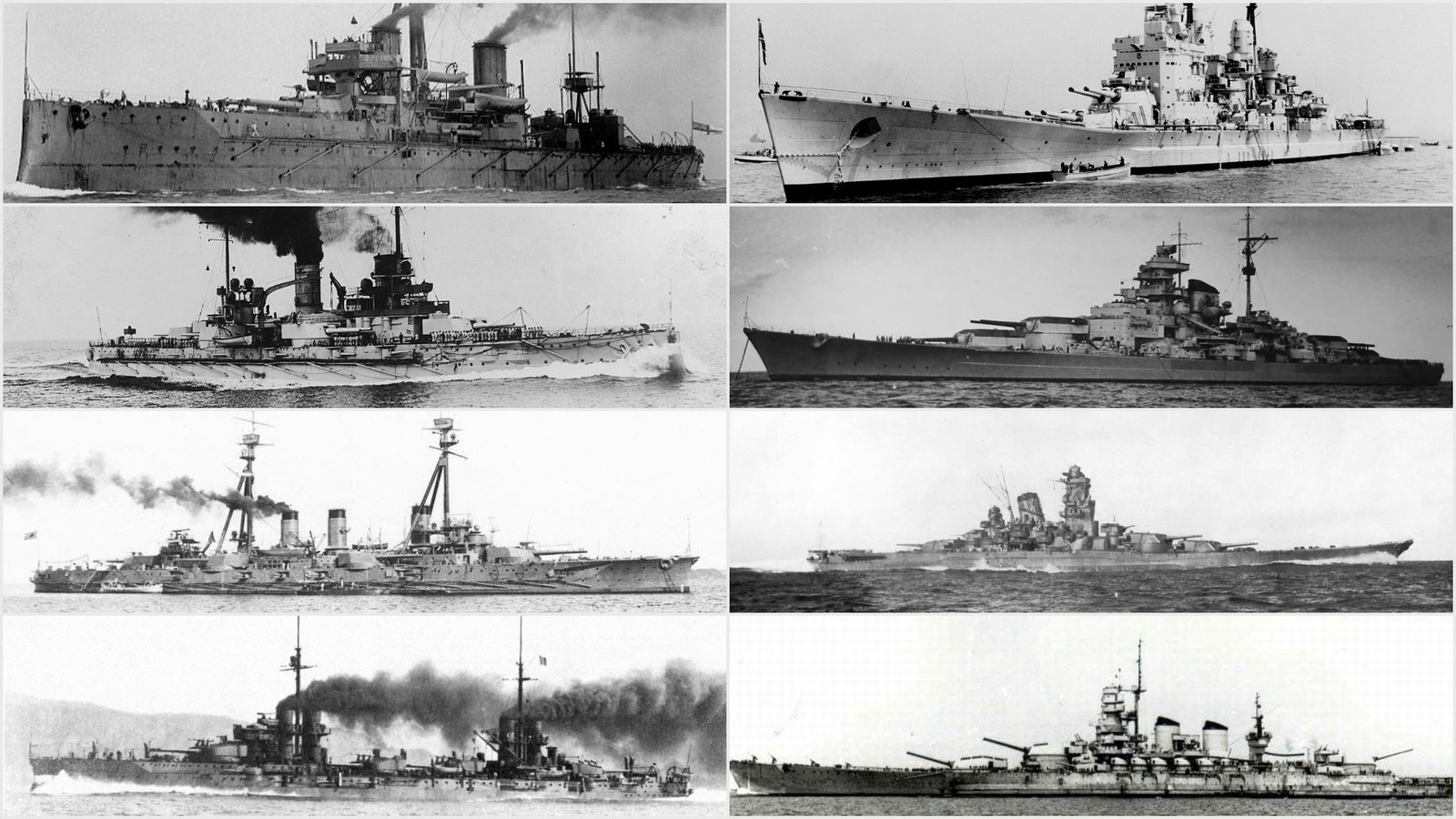
A Shift in Naval Warfare Strategies
The Rise of Aircraft Carriers
A pivotal factor contributing to the retirement of battleships was the emergence of aircraft carriers as the centerpiece of naval power projection. Aircraft carriers offered unmatched versatility, long-range strike capabilities, and the ability to conduct sustained operations far from shore. The advent of carrier-based aircraft allowed for more efficient and precise delivery of firepower, rendering battleships less essential in modern warfare.Naval Gunfire Support Evolution
Another crucial aspect that influenced the retirement of battleships was the evolution of naval gunfire support (NGFS) techniques. While battleships were historically relied upon for NGFS, advancements in missile systems, precision-guided munitions, and close air support planes presented more effective alternatives. These new technologies allowed for greater accuracy, flexibility, and reduced risk to naval assets.The Effectiveness of Modern Naval Platforms
Missile Systems and Guided Munitions
Modern naval platforms, such as destroyers and cruisers, are equipped with advanced missile systems capable of striking targets with precision and from extended ranges. These systems offer a more cost-effective solution compared to battleships, as they can engage multiple targets simultaneously and provide enhanced capabilities in anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine warfare scenarios.Versatile Naval Surface Combatants
The U.S. Navy has transitioned to versatile naval surface combatants, such as guided-missile destroyers and cruisers, which offer a range of capabilities suited to today’s complex threats. These platforms incorporate advanced sensors, command and control systems, and integrated warfare capabilities, allowing for seamless coordination with other naval assets and joint forces. The multi-mission nature of these vessels ensures adaptability across a wide spectrum of operations.Cost Considerations and Fleet Modernization
Budgetary Constraints
The cost of maintaining and operating battleships played a significant role in their retirement. Battleships required substantial resources for crewing, maintenance, ammunition, and logistical support. As the Navy faced budgetary constraints and evolving strategic priorities, allocating resources to more versatile and cost-effective platforms became imperative.Fleet Modernization and Force Structure
The retirement of battleships allowed the Navy to prioritize fleet modernization efforts. The reallocation of resources enabled the procurement and development of advanced platforms, including aircraft carriers, submarines, amphibious assault ships, and guided-missile destroyers. This modernization strategy enhanced the Navy’s capabilities across a broader range of missions, including power projection, sea control, and maritime security.Conclusion
The retirement of battleships from the U.S. Navy represents a significant shift in naval warfare strategies and the evolution of modern naval platforms. The rise of aircraft carriers, advancements in missile systems, and the need for more versatile and cost-effective assets have led to battleships becoming obsolete in contemporary naval operations. The Navy’s focus on fleet modernization and the development of multi-mission platforms has ensured the maintenance of maritime superiority in an ever-changing global security landscape.