Overview
What is meant by a sustainable city improvement?
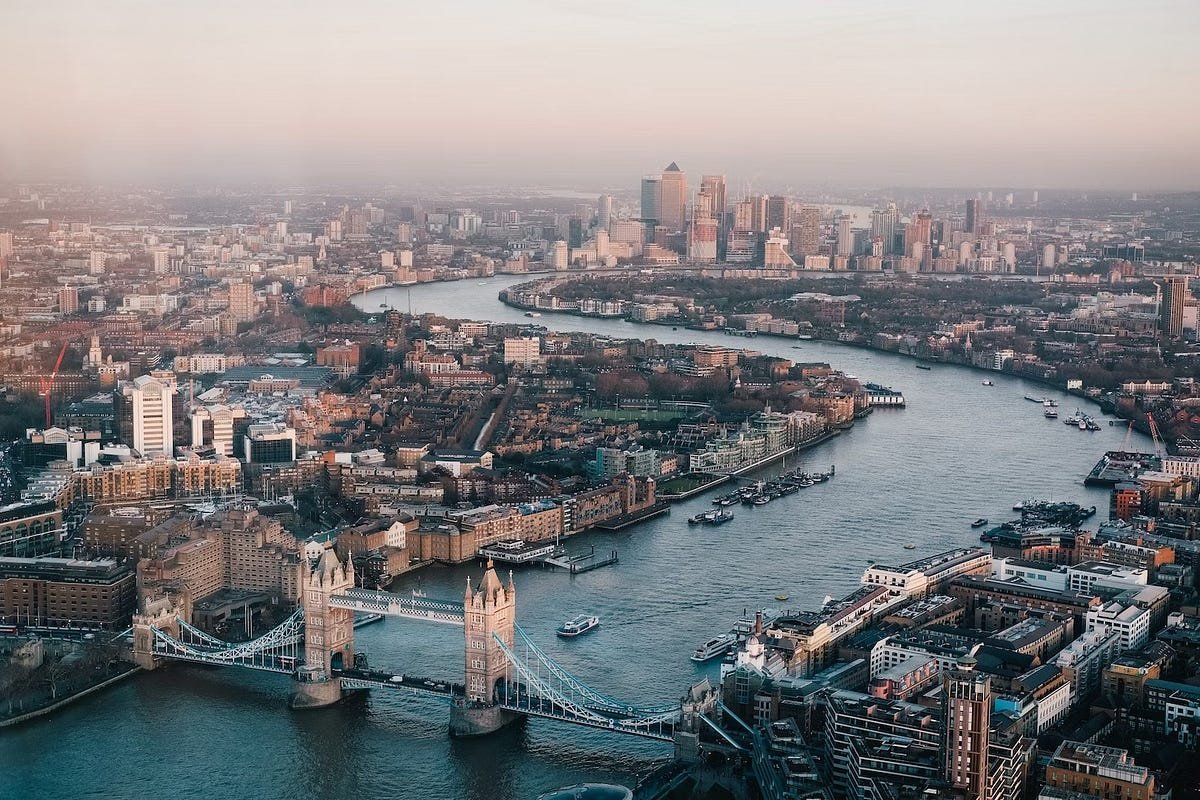
The method of making plans and managing towns if you want to meet the demands of the present without endangering the capacity of destiny generations to fulfill their personal requirements is known as sustainable urban improvement. In order to produce resilient and colorful city environments, it contains a holistic approach to city making plans and development that integrates monetary, environmental, and social elements.
Technology’s Role in Urban Sustainability
In order to facilitate sustainable city boom, generation is crucial. It makes useful resource management more powerful, lessens its terrible consequences at the surroundings, and improves city dwellers’ first-rate lifestyles. Innovations in this era, ranging from smart infrastructure to renewable electricity systems, are important for conquering urbanization’s boundaries and achieving sustainability objectives.
Smart Cities: The Urban Living of the Future
Smart Cities: What Are They?
Digital generation and records analytics are utilized in clever towns to sell sustainable development, increase useful resource performance, and enhance municipal offerings. These cities build responsive, adaptive, and sustainable urban ecosystems via the use of synthetic intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and different modern-day generations.
Important Aspects of Smart Cities
Integrated infrastructure, real-time statistics gathering and analysis, and citizen-centric offerings are a number of the important traits of clever towns. The purpose of clever cities is to maximize city functions like public safety, waste control, strength distribution, and transportation. For example, clever lighting fixtures structures can use much less strength, while smart traffic control systems can reduce pollution and traffic jams.
Technological trends supporting sustainable improvement: few examples
Technological improvements are vital for promoting sustainable development due to the fact they offer solutions to problems associated with the surroundings. The tremendous use of renewable energy technology, together with hydropower, wind, and sun power, is one instance.
By offering clean and renewable power resources in the vicinity of fossil fuels, these technologies help reduce greenhouse fuel emissions and our reliance on confined assets. Energy-efficient creation and transportation structures help to promote sustainable development by means of decreasing carbon emissions and strength usage.
Furthermore, waste management technologies, including recycling and waste-to-energy techniques, resource in the reduction of garbage in landfills and the development of resource efficiency. With technology like sensors, drones, and facts analytics, precision agriculture enables farmers to maximize aid usage, reduce their effect on the surroundings, and sustainably beautify agricultural yields.
Particularly in areas where water is scarce, smooth water technology like desalination centers and complicated filtration structures guarantee access to secure and smooth drinking water. These examples show how technical improvements, with the aid of tackling principal issues in strength, waste control, agriculture, and water resources, are important for fostering sustainable improvement and environmental conservation.
Technology’s role in decreasing carbon emissions and preventing weather trade
Through its capability to offer innovative solutions in quite a few industries, era is crucial in the combat towards climate exchange and in reducing carbon emissions. Innovations in renewable power technologies, which includes wind and solar electricity, allow us to move away from fossil fuels, which can be the principal reason for greenhouse fuel emissions. This has a primary effect at the strength area.
Lower carbon footprints are also a result of strength-efficient production, transportation, and industrial era. The integration of intermittent renewable strength sources is improved by means of clever grids and power garage technology, which further lessens dependency on fossil fuels.
Additionally, trends in the carbon seize and storage era present feasible approaches to reduce emissions from electricity plant life and enterprise. In addition to the strength industry, era promotes environmentally pleasant agricultural, waste control, and urban layout techniques that lower emissions and increase resistance to the results of weather change.
But there are barriers to the wide use of these technologies, inclusive of money, infrastructural needs, and regulatory backing. Despite these barriers, meeting the lofty desires outlined within the fight in opposition to weather alternate and the development of sustainable development depends on the continuing invention and alertness of technology.
Integration of Renewable Energy: Solar and Wind Power in Urban Environments
Urban areas must incorporate renewable electricity resources, consisting of sun and wind strength, to reduce carbon emissions and enhance strength safety. There are many capacity in city settings to integrate wind mills at key regions and install sun panels on rooftops. These renewable power tasks can inspire sustainable power consumption and notably lessen dependency on fossil fuels.
Energy Management and Smart Grids
Smart grids are sophisticated strength networks that efficiently monitor and control the drift of strength through the use of virtual technology. They make it viable to encompass renewable energy assets and make adjustments to electricity use in real time. In order to make certain a constant and sustainable energy delivery, clever grids also provide energy garage technologies, which enable excess energy generated at some stage in top hours to be stored and used later.
Eco-Friendly Mobility Options
Autonomous and Electric Automobiles
The use of self-sufficient vehicles (AVs) and electric vehicles (EVs) is revolutionizing city transportation by way of cutting greenhouse gas emissions and increasing traffic flow. While AVs provide the promise for safer and greater effective transportation structures through more suitable navigation and communique technologies, EVs help to enhance the satisfaction of the air.
Innovations in Public Transportation
Smart transit structures and electric buses are two examples of public transportation innovations which can be essential for sustainable urban mobility. These trends improve public transportation’s accessibility and convenience at the same time as lessening the negative environmental outcomes of mass transit. Additionally, commuters might also plan their trips extra successfully with the useful resource of phone packages and real-time data.
Infrastructure That Is Pedestrian and Bicycle Friendly
Creating an environment that encourages taking walks and bicycling is important to sustainable urban growth. Bicycle-sharing schemes, pedestrian zones, and motorcycle lanes promote environmentally friendly transportation and lessen dependence on automobiles. By encouraging lively existence, these applications additionally enhance public fitness.
Energy-efficient building materials and green building technologies
Buildings can consume less energy when energy-efficient materials are used, such as low-emissivity glass and insulated concrete forms. These materials reduce the need for heating and cooling, improve thermal insulation, and produce less greenhouse gas emissions. It is imperative for sustainable building methods to integrate these materials into urban construction.
Systems for Smart Building Management
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, lighting, and other building activities are monitored and managed by smart building management systems (BMS) through the use of sensors and automation. These technologies increase occupant comfort, optimize energy use, and improve indoor air quality. In urban structures, BMS can drastically save operating expenses and energy waste.
Green roofs and vertical gardens
Green roofs and vertical gardens are creative approaches to urban greening. By incorporating vegetation onto building facades and rooftops, these systems enhance air quality, decrease the impact of the urban heat island, and provide natural insulation. In addition to promoting biodiversity, green roofs improve the visual attractiveness of metropolitan settings.
Conservation and Management of Water
Intelligent Water Systems
IoT technology is used by smart water grids to monitor and control water distribution networks. These grids make sure that water is used efficiently, maximize water pressure, and identify leaks. Smart water networks aid in sustainable urban water management by lowering water loss and improving distribution efficiency.
Collecting Rainwater and Recycling Greywater
Greywater recycling and rainwater harvesting systems collect and repurpose water for uses other than drinking, like toilet flushing and irrigation. These methods ease the burden on urban water sources and lower the demand for fresh water. Water conservation and sustainability in urban areas greatly depend on the adoption of such technology.
IoT for Detecting Water Leaks
Urban infrastructure water leaks can be found and identified using sensors and real-time data analytics via IoT-enabled leak detection systems. Leaks should be found and fixed as soon as possible to avoid wasting water and lower the chance of infrastructure damage. For cities to continue managing their water resources sustainably and effectively, these systems are essential.
Innovative Waste Management
Intelligent Trash Collection Systems
Garbage collection routes and schedules are optimized by smart garbage collection systems using sensors and data analytics. These devices limit fuel usage, cut emissions, and save operating costs. Furthermore, real-time waste level information may be obtained from smart bins, guaranteeing prompt collection and avoiding overflow.
Technologies for Recycling and Waste-to-Energy
Waste-to-energy (WtE) systems and cutting-edge recycling techniques transform waste materials into useful resources and energy. These innovations encourage a circular economy, cut greenhouse gas emissions, and lessen the use of landfills. Sustainable waste management in urban areas requires the use of recycling and WtE solutions.
Data Analytics and Urban Planning: The Significance of Big Data in Urban Planning
Urban planning greatly benefits from big data analytics’ ability to provide light on population trends, traffic patterns, and infrastructure requirements. Cities can make well-informed decisions, allocate resources optimally, and enhance overall urban sustainability through data-driven urban planning.
Predictive Analytics in the Development of Infrastructure
Predictive analytics forecasts future urban requirements and issues using machine learning algorithms and historical data. These resources support city planners in anticipating infrastructure needs, making plans for population expansion, and reducing risks. Building resilient and flexible urban environments is made possible in large part by predictive analytics.
Public Participation through Digital Platforms for Smart Governance and Citizen Engagement
By allowing citizens to access public services, offer input, and take part in urban planning processes, digital platforms promote citizen involvement. These platforms create a feeling of community and shared responsibility for urban development by encouraging openness, inclusivity, and cooperation between residents and city leaders.
Smart Services and E-Governance
Technology is used by e-government projects to deliver effective and easily accessible public services. The utilization of online portals, mobile applications, and automated systems can optimize administrative procedures, mitigate bureaucratic obstacles, and improve service provision. A key component of smart governance and sustainable urban development is e-government.
Difficulties and Opportunities for the Future
Financial and Technological Barriers
Implementing sustainable urban tech faces high costs, regulatory challenges, and complex technology demands. Public-private collaborations, supportive policies, and strategic planning are necessary to remove these obstacles. Scaling sustainable urban solutions requires addressing these issues.
Upcoming Development Trends in Sustainable Urban Areas
Future trends in sustainable urban development include AI advancements, IoT network growth, and increased renewable energy use. Urban environments will continue to be shaped by these tendencies, which will encourage sustainability and creativity. It is essential to adopt these trends if sustainable cities are to continue to progress.
The Future Direction of Ecological Urban Development
Cities must use technology holistically to tackle social, economic, and environmental issues for sustainable urban growth. Governments, corporations, and residents must collaborate to create sustainable urban environments for present and future needs.
Summary
Technology integration is essential to sustainable urban development in order to build livable, efficient, and resilient cities. Key sectors: smart cities, data analytics, green building, waste management, renewable energy, sustainable transport, water management, citizen involvement. The success of sustainable urban development will be ensured by overcoming obstacles and embracing emerging trends.
FAQ
Q: Sustainable urban development: what is it?
A: In order to ensure the welfare of present and future generations, sustainable urban development entails developing urban environments that are economical with resources, ecologically benign, and inclusive of all social groups.
Q: What role does technology play in the creation of sustainable urban areas?
A: By boosting resource management, lessening environmental impact, and improving the quality of urban life through technologies like smart cities, renewable energy, and data analytics, technology promotes sustainable urban development.
Q: Smart cities: what are they?
A: Digital technologies and data analytics are employed in smart cities to optimize urban services, improve resource efficiency, and foster sustainable growth.
Q: What are some ways to incorporate renewable energy into cities?
A: By installing solar panels, wind turbines, and smart grids that efficiently regulate and distribute electricity, renewable energy may be incorporated into metropolitan settings.
Q: Which modes of transportation are sustainable?
A: Innovative public transit systems, infrastructure that encourages cycling and walking, and electric and driverless vehicles are examples of sustainable transportation options.
Key Takeaway
Technology ensures sustainable urban development by improving resource management, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing urban living. Future generations need stakeholders to collaborate and embrace technological breakthroughs for resilient, prosperous urban environments.