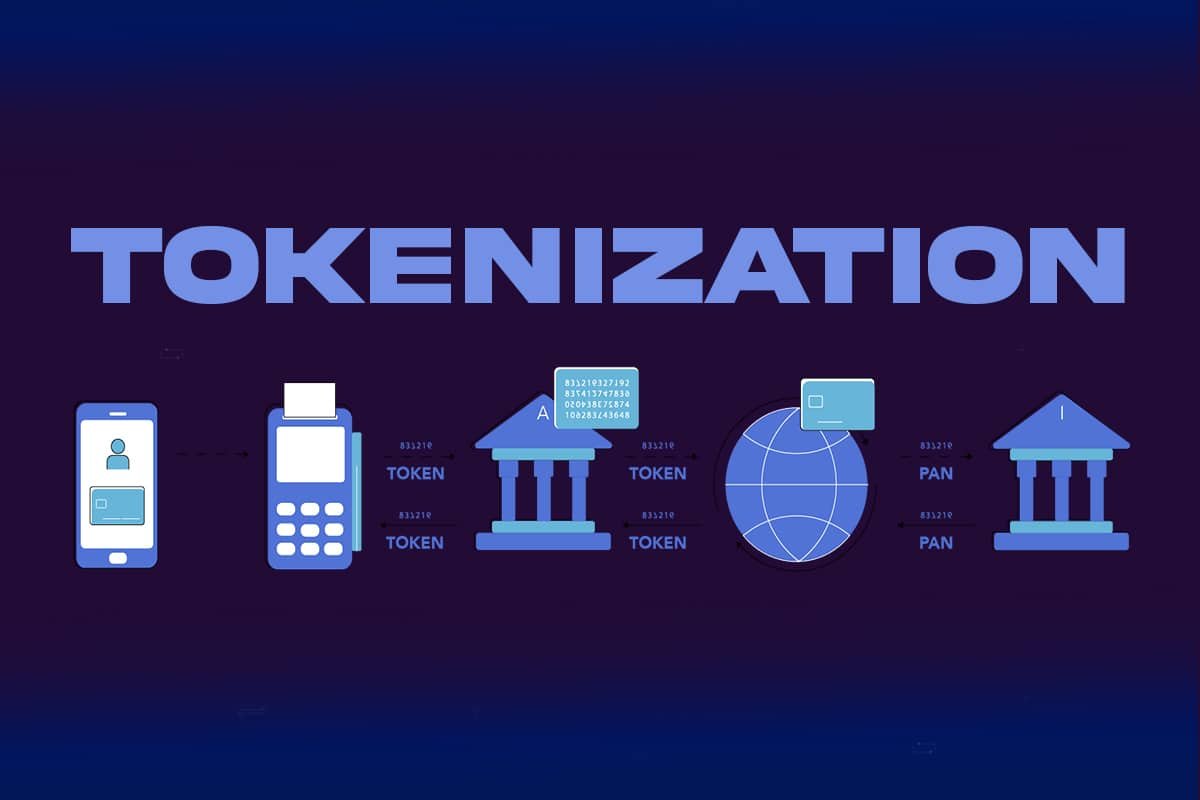
Overview
Over the past ten years, there has been a giant alternative inside the virtual bills market. A simple method that concerned credit score playing cards and real foreign money has advanced into a sophisticated web of net transactions, contactless payments, and mobile wallets. Tokenization, a generation that is revolutionizing how we method payment security and efficiency, is at the middle of this change.
Even though the word “tokenization” is relatively new within the financial industry, it’s a key generation with a view to affect digital transactions going ahead. Sensitive payment statistics are substituted with wonderful, non-touchy tokens which might be secure to apply on numerous fee structures. This era makes digital and mobile payments easier to procedure at the same time as also enhancing safety. We will have a look at tokenization on this post, consisting of its definition, operation, advantages, drawbacks, and ability programs.
What does tokenization suggest?
Tokenization is a safety method that substitutes a non-touchy token for sensitive records, which include credit card numbers or private information, defending the latter. The tokenization substitutes sensitive information in the price surroundings with a unique identifier or token, in place of encryption, which encrypts statistics using algorithms.
Tokenization: An Overview and Definition
The system of turning sensitive data into a token that may be used in regions of unique information is called tokenization. For example, a commercial enterprise would possibly store a randomly generated token that maps lower back to the authentic information thru a secure token vault, in place of the credit card records of a patron.
Comparing Tokenization and Encryption
Data is encrypted using algorithms that can be unlocked with a key, restoring it to its authentic kingdom.
Tokenization: This method replaces confidential information with a token that is nugatory and cannot be reverted to its authentic shape without a token vault.
Tokenization ensures protection with the aid of taking sensitive information out of the payment context and setting it someplace else, while encryption secures statistics by transforming it via problematic mathematical operations. This distinction is essential for the reason that the aim of tokenization is to lessen the quantity of sensitive facts that is uncovered.
How Tokenization Operates
Tokenization includes some of the essential techniques to guarantee the secure control of touchy statistics at some stage in the charge procedure. The way tokenization features inside the context of price processing is as follows:
- Data collection: When a patron begins a transaction, they supply the employer their credit score card data and different price information.
- Tokenization request: The sensitive statistics may be sent to a secure tokenization service, commonly provided by using a fee processor or a 3rd-party tokenization seller, relying on how the commercial enterprise’s payment device is configured. Tokenization is an inherent thing of payment processing whether the agency is utilizing Stripe Terminal or other hardware or software that helps tokenization.
- Token generation: Tokenization creates a completely unique token that symbolizes the authentic fee records by way of combining a number of encryption techniques, steady storage techniques, and algorithms. Usually, this token is only a random string of letters or integers that has no significance or inherent real worth outside of the precise price system.
- Storage of tokens: The business’s device stores tokens in the location of touchy price records. The tokenization provider’s steady vault, that is intended to shield it from illegal get admission to and facts breaches, is where the unique charge facts are stored securely.
- Usage of tokens: The organization can publish the token to the payment processor or tokenization company which will conduct the transaction. After that, the carrier safely hyperlinks the token to the preliminary payment statistics, enabling the transaction to be completed without disclosing any private information to the organization or different middlemen.
- Token reusability: The identical token can be used again and again for routine transactions (such subscriptions or saved client profiles) without obtaining sensitive charge information every time. This keeps the whole lot steady however streamlines the charge system.
Overview of the Process: Creation and Mapping of Tokens
Token Mapping: Next, in a secure token vault, the token is mapped to the unique touchy facts.
Token Decryption: The TSP can hint a token back to the authentic facts if necessary, however handiest in the secure haven of the TSP vault.
Which companies require tokenization as a payment technique?
Tokenization provides noteworthy blessings for a range of businesses coping with confidential fee records. Among them are:
- Tokenization lowers the hazard of fraud and safety breaches in online transactions, which benefits e-trade companies via protecting consumer payment records.
- Services that require a subscription: Tokenization can be utilized by companies that provide habitual billing to safely manipulate consumer charge statistics for non-stop transactions.
- Physical store outlets: Tokenization can assist physical institutions in the usage of factor-of-sale (POS) structures or cellular charge answers, even though it’s miles more customary in online transactions, by adding a further degree of protection.
- Marketplaces and platforms: Payment tokenization fosters scalability inside the operations of platform companies through enhancing protection and streamlining the administration of touchy charge facts for various events collaborating in complicated transactions.
Token Service Providers’ (TSPs’) role
Token creation and management fall below the purview of TSPs. They oversee the tokenization process and hold touchy statistics safe in a vault. Token safety protocol (TSP) guarantees that tokens are distinct, irreversible, and securely mapped to the original data only while required. Tokenization services are provided to banks, traders, and charge processors by predominant TSPs together with Visa, Mastercard, and American Express.
Advantages of Tokenization
Tokenization gives some benefits that enhance price systems’ safety and effectiveness.
Strengthened Security: Avoiding Data Breach
Tokenization’s ability to shield personal charge information from records breaches is certainly one of its essential benefits. Tokenization makes sure that even in the event of a breach, the stolen tokens can’t be used for fraudulent transactions by substituting a token with no actual cost for touchy statistics.
For example, if a hacker manages to get into a service provider’s tokenized price database, all they will have are tokens which are in vain inside the absence of the related information that is kept safe in the TSP’s vault.
Enabling Digital and Mobile Payments
Additionally, tokenization promotes the growth of virtual and mobile bills. Tokenization permits users to conduct safe transactions using contactless charge methods and mobile wallets without disclosing their actual fee details.
For instance, the user’s credit score card statistics is tokenized and substituted with a wonderful token while utilizing Apple Pay or Google Pay. Tokens are used for transactions in preference to real card numbers, improving safety and making cellular bills clean.
Regulations and Standards for Tokenization
To ensure the efficiency and security of tokenization, some of industry standards and legal guidelines function.
Summary of Industry Standards (EMVCo Tokenization Framework, as an instance)
A popular tokenization technology was created by means of the industry consortium of most important credit card networks, EMVCo, and is referred to as the EMVCo Tokenization Framework. Best practices for tokenization, such as token advent, lifecycle control, and token vault security, are defined in this framework.
Main Components of the Structure:
Requester of Tokens (TR): The entity making the token request.
Token Service Provider (TSP): Organization in fee of creating and retaining tokens.
Token Vault: A secure haven for token mapping and the garage of private information.
Adherence to PCI DSS and Additional Regulations
Tokenization needs to abide by way of the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), which establishes pointers for defensive cardholder statistics. Since touchy price records isn’t bodily processed or saved, tokenization narrows the region of compliance and allows traders and price processors to conform with PCI DSS regulations.
Tokenization Across Various Payment Processes
To improve safety and expedite the payment method, tokenization is used with quite a few price mechanisms.
Tokenization for Payments with Credit and Debit Cards
Tokenization substitutes a wonderful token for the credit score or debit card range in conventional credit and debit card transactions. This procedure guards cardholder information in opposition to possible robbery in each in-individual and online transactions.
Example:
Your actual credit card information is protected against publicity when you input your card variety on an e-trade website due to the fact the card variety is tokenized and transmitted as a token.
Combining NFC Technology and Mobile Wallets
Near Field Communication (NFC) era and mobile wallets each depend on tokenization. Tokenization is used by cellular wallets which includes Apple Pay and Google Pay to provide secure, contactless bills.
For instance, your cell pockets creates a token that is equal on your card records while you faucet your phone at a contactless charge terminal. This allows you to make a purchase without disclosing your actual card statistics.
Obstacles and Restrictions
Tokenization has several advantages, however there also are some troubles and restrictions that ought to be resolved.
Implementation Difficulties for Payment Processors and Merchants
Tokenization implementation might be hard for fee processors and stores. Tokenization solutions should be incorporated into their present day charge structures, which can be expensive and technically hard.
For instance, which will assist tokenization, merchants need to update their point-of-sale structures and payment gateways. This may also contain a vast funding in new generation and worker training.
Problems with Scalability and Their Remedies
Another difficulty with tokenization is scalability, specifically for large groups with plenty of transactions. Large transaction volumes ought to now not compromise performance in the tokenization infrastructure.
Example: To cope with scalability, numerous TSPs offer cloud-based tokenization services that permit corporations control charges and performance with the aid of scaling up or down depending on transaction volumes.
Prospective Patterns in Tokenization
It is predicted that tokenization will improve and turn out to be an increasing number of important digital payments within destiny.
Tokenization’s Contribution to the Growth of Contactless Payments
Tokenization will remain a crucial device to assure stable transactions as contactless payments gain traction.
Tokenization will be necessary, for instance, as contactless charge techniques—like clever playing cards and digital wallets—proliferate on the way to protect fee data and enhance consumer comfort.
Technological Advancements in Tokenization (inclusive of Dynamic Tokens)
To similarly improve protection, future improvements in tokenization technology may contain dynamic tokens that vary with each transaction.
For example, dynamic tokenization creates a new token for each transaction, which makes it extra hard for scammers to use tokens they’ve stolen for nefarious purposes.
Examples and Case Studies
A variety of actual instances show how successful tokenization is in price systems.
Implementations in Major Payment Systems That Are Successful
- Apple Pay: During transactions, Apple Pay protects purchasers’ credit score card statistics with tokenization. To ensure that shops are not exposed to the card quantity, each transaction creates a completely unique token.
- Visa Token Service: Tokens are utilized in regions of card numbers in Visa’s tokenization provider to improve online and cell transaction safety.
Tokenization’s Effect on Fraud Reduction
Because tokenization reduces the hazard of touchy facts being uncovered, fraud in fee structures has been significantly decreased.
For example, tokenization can cut card-not-present fraud by as much as 60% in markets wherein it is used, according to studies by means of EMVCo.
FAQ concerning Tokenization
Q: When it comes to payment security, what are tokens?
A: Credit card numbers and other sensitive payment information are replaced with randomly generated tokens. In order to safeguard information during transactions and stop fraud, they are utilized in place of actual data.
Q: In what ways does tokenization prevent fraud?
A: By eliminating critical payment information from the transaction process, tokenization guards against fraud. To mitigate the danger of fraudulent transactions and data breaches, sensitive data is safely held in a token vault and only the token is transferred.
Key Takeaway
One revolutionary technique that is essential to contemporary payment systems is tokenization. By supporting industry standards and laws, enabling safe mobile and digital payments, and substituting unique tokens for sensitive data, it improves security. Tokenization will continue to be an essential technique as digital payments develop, with upcoming advancements focused on enhancing security and transaction effectiveness.
Important lessons learned:
- Security: By safeguarding sensitive data, tokenization greatly improves payment security.
- Efficiency: It facilitates the expansion of digital and mobile payments by allowing safe, easy, and seamless transactions.
- Compliance: Tokenization narrows the scope of PCI DSS compliance and assists organizations in meeting regulatory standards.
- Future Trends: The future of tokenization will be shaped by innovations such as dynamic tokens and the growth of contactless payments.
- At the forefront of payment security technology, tokenization provides answers for present problems as well as potential future developments in the payments sector.
The definition, advantages, difficulties, and potential developments of tokenization in payments are all covered in detail in this extensive article. In order to assist readers comprehend the significance of tokenization in contemporary payment systems, it also offers real-world examples and addresses frequently asked concerns.